NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被103位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。
NMT历史上的今天
2011年11月25日,山东省农科院董合忠、孔祥强利用NMT在Journal of Experimental Botany 上发表了标题为Effects of non-uniform root zone salinity on water use Na+ recirculation, and Na+ and H+ flux in cotton的研究成果。

期刊:Journal of Experimental Botany
主题:根系不均一盐胁迫提升植物水分利用率的机制
标题:Effects of non-uniform root zone salinity on water use Na+ recirculation, and Na+ and H+ flux in cotton
影响因子:4.818
检测指标:Na+、H+流速
作者:山东省农科院董合忠、孔祥强
英文摘要
A new split-root system was established through grafting to study cotton response to non-uniform salinity. Each root half was treated with either uniform (100/100 mM) or non-uniform NaCl concentrations (0/200 and 50/150 mM).
In contrast to uniform control, non-uniform salinity treatment improved plant growth and water use, with more water absorbed from the non- and low salinity side. Non-uniform treatments decreased Na+ concentrations in leaves. The [Na+] in the ‘0’ side roots of the 0/200 treatment was significantly higher than that in either side of the 0/0 control, but greatly decreased when the ‘0’ side phloem was girdled, suggesting that the increased [Na+] in the ‘0’ side roots was possibly due to transportation of foliar Na+ to roots through phloem.
Plants under non-uniform salinity extruded more Na+ from the root than those under uniform salinity. Root Na+ efflux in the low salinity side was greatly enhanced by the higher salinity side. NaCl-induced Na+ efflux and H+ influx were inhibited by amiloride and sodium orthovanadate, suggesting that root Na+ extrusion was probably due to active Na+/H+ antiport across the plasma membrane.
Improved plant growth under non-uniform salinity was thus attributed to increased water use, reduced leaf Na+ concentration, transport of excessive foliar Na+ to the low salinity side, and enhanced Na+ efflux from the low salinity root.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
通过嫁接建立了一个新的分根系统,以研究棉花对盐度不均匀的响应。每个根部均用均一的(100/100 nonmM)或不均一的氯化钠浓度(0/200和50/150 mM)处理。
与统一控制相反,非均匀盐度处理改善了植物生长和水分利用,从非盐度和低盐度侧吸收了更多的水。不均匀处理降低了叶片中的Na+浓度。0/200处理的'0'侧根中的[Na+]显着高于0/0对照中任一侧的[Na+],但当'0'侧韧皮部被束腰时,其[Na+]大大降低,表明[ [0]侧根中的Na+]可能是由于叶面Na+通过韧皮部转运至根。
盐度不均匀的植物比盐度均匀的植物从根部挤出的Na+更多。低盐度一侧的根Na+流出量被高盐度一侧大大增强。NaCl诱导的Na+流出和H+流入被阿米洛利和原钒酸钠抑制,这表明根Na+的挤出可能是由于跨质膜的活性Na+ / H+逆向转运所致。
因此,在非均匀盐度下植物生长的改善归因于增加的水分利用,降低的叶片Na+浓度,过量的叶面Na+向低盐度侧的运输以及从低盐度根部提高的Na+外排。
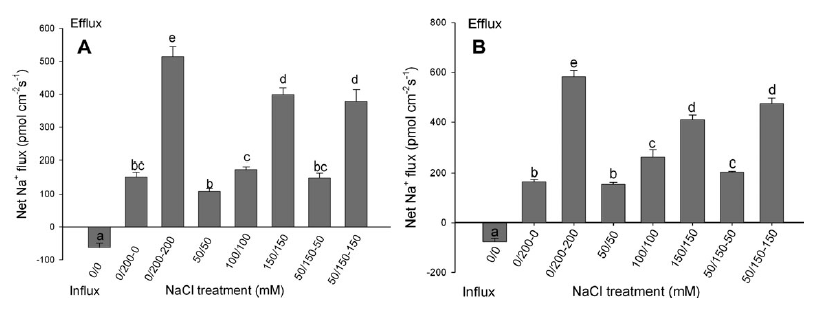
Effects of non-uniform (0/200 mM and 50/150 mM NaCl) and uniform (0/0, 50/50, 100/100, and 150/150 mM NaCl) root zone salinity on net Na+ fluxes in roots of cotton at 1 d (A) and 7 d (B) after treatment. The data are main fluxes of Na+ within the measuring periods (15 min). Values are means 6SE (n¼6). Bars with different letters (a, b, and c) differ significantly at P < 0.05.
文章链接:
https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/63/5/2105/531495?searchresult=1
